Revealing The Key Issues Of Emulsification Pumps
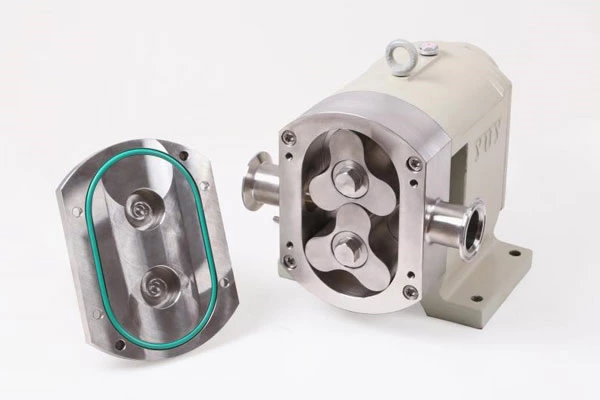
Emulsification Pump The sealing ring loses its elasticity due to long-term use. At this time, the sealing ring can be removed, and then a piece of paper or cloth with a thickness of 0.3 to 0.5 mm can be cut into a pad slightly larger than the original sealing ring and installed in the groove, and finally the original sealing ring can be installed. If the rubber sealing ring in the nylon sealing seat is worn, the sealing ring can be removed and then installed in a different position. If the fastening spring on the sealing ring loses its elasticity or breaks, the spring can be removed and tightened with a steel wire or iron wire of appropriate diameter. If the rubber sealing ring of the oil hole is damaged, a piece of adhesive tape can be found, cut into a hole slightly larger than the bolt, and a flat pad can be added on top, and then put together in the bolt oil inlet hole. If the sealing ring between the sealing box and the cast iron of the emulsification pump loses its elasticity, the sealing ring can be removed from the cast iron groove, and a piece of cardboard with a thickness of 0.6 to 1 mm can be cut into the same size, and pad in the groove, and then the sealing ring can be put in.
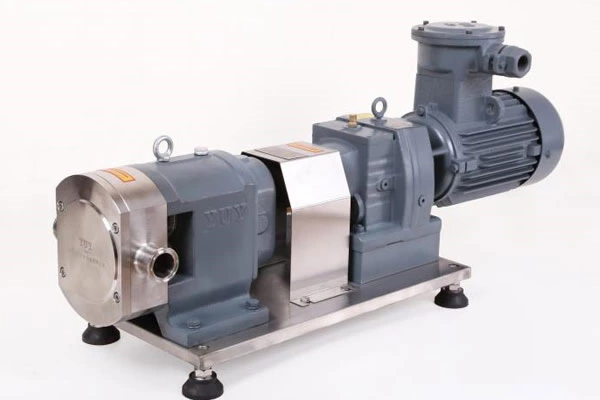
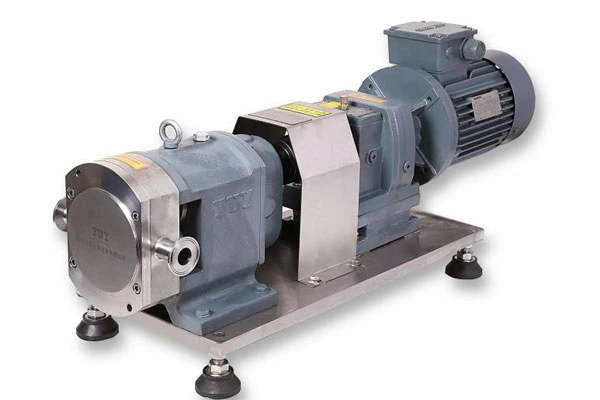
It is necessary to set up a protection system in the emulsification pump, which can effectively protect the safe operation of the electric pump. But this is not the crux of the problem. The protection system is just a remedy after the pump fails, which is a relatively passive method. The most critical issue for the emulsification pump is reliability, because the medium to be transported is a mixed liquid containing solid materials. This problem makes the requirements of the emulsification pump in terms of sealing, motor load capacity, bearing arrangement and selection higher than those of general pumps. Therefore, when selecting, it is necessary to understand the sealing reliability and load capacity of the emulsification pump.
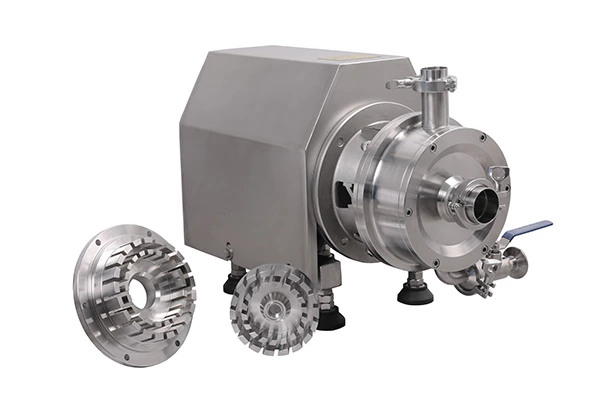
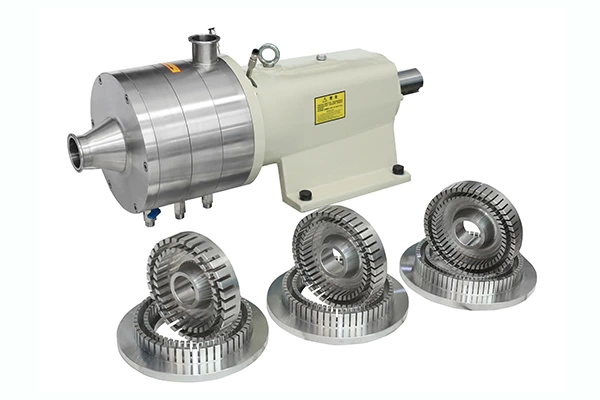
The emulsification pump adopts a unique double-suction double-channel structure. In actual operation, the water enters from both ends of the water pump impeller and flows out from the middle. The water inlet of the water pump is divided into upper and lower parts, and both draw water from the bottom. The water suction direction is low. Because water is sucked from the upper and lower ends, one end of the isolation oil chamber between the pump and the motor is at the water suction port position. It is always in a negative pressure state during operation. It is not easy to leak compared to the single-suction structure. Because the pump sucks water from both ends at the same time, the motor has no axial tension, and the double-channel structure reduces the radial force, thereby extending its service life and achieving the functions of durability, stability and practicality.
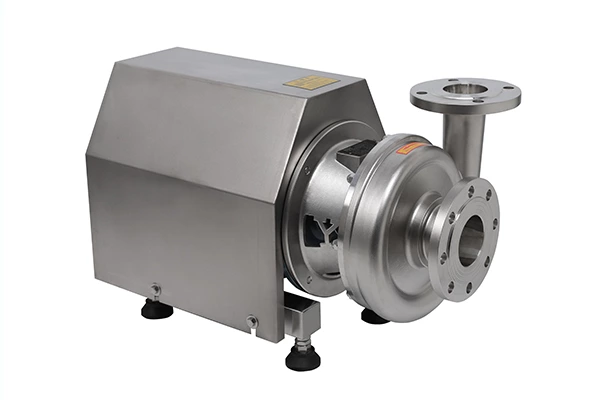
The vertical motor of the emulsification pump is fastened to the motor base with bolts, and is directly driven by the pump through an elastic coupling. The pump body, intermediate pipe, pump frame, liquid outlet pipe, and pipe flange are bolted together and fixed on the base plate. The entire pump is installed on the container through the base plate. The axial force and radial force of the pump (including the water pressure generated during the operation of the pump, the weight of the impeller and rotor, etc.) are all borne by the one-way thrust ball bearing, single-row radial ball bearing installed in the bearing box; and the sliding guide shaft to ensure the safe and normal operation of the pump. The bearings are lubricated with butter, and the guide bearings are lubricated with the liquid being transported. Therefore, the liquid level must be higher than the center line of the impeller when the emulsification pump is working. The length L of the extension into the container is different, and it is divided into an intermediate guide bearing structure and a structure without an intermediate guide bearing.