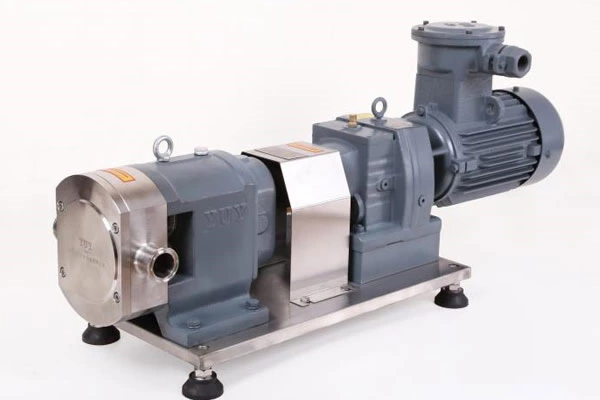
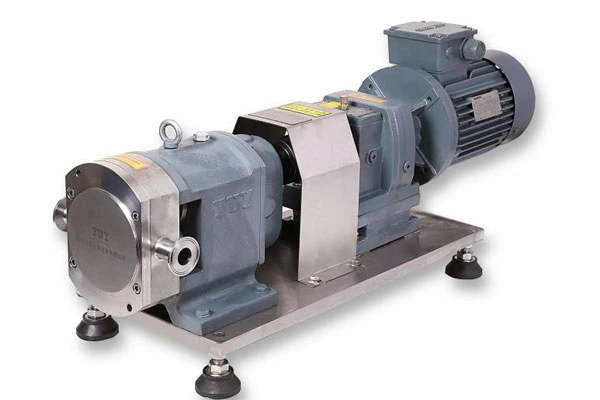
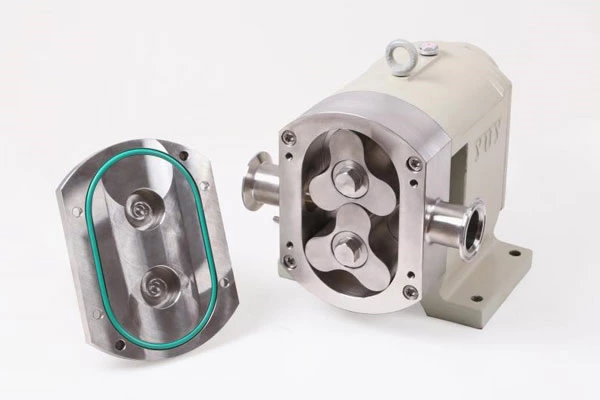
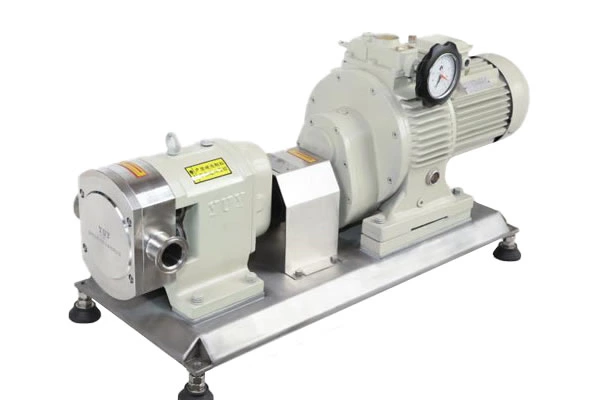
Industrial Pump Products And Chemical Centrifugal Pump Material Selection Considerations According To Use
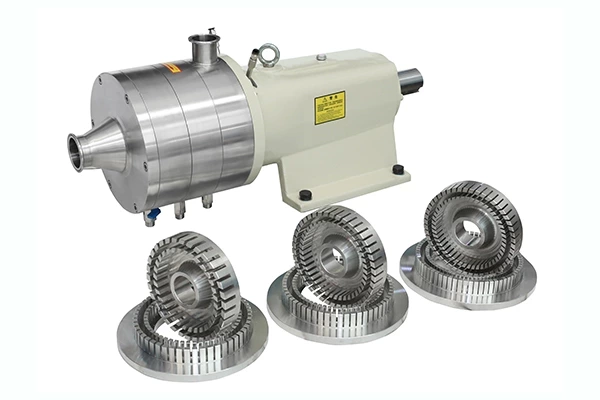
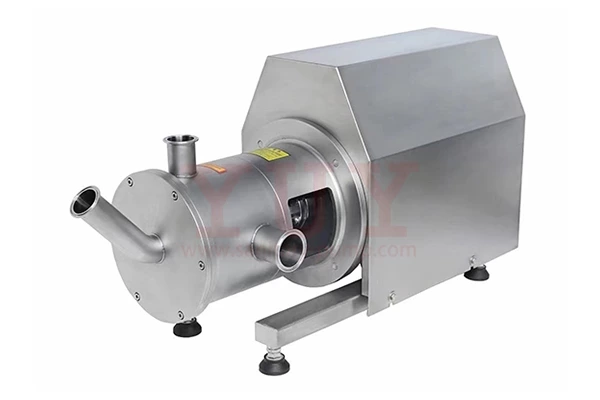
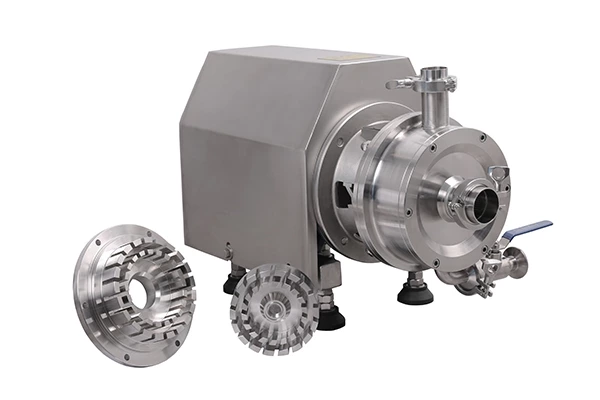
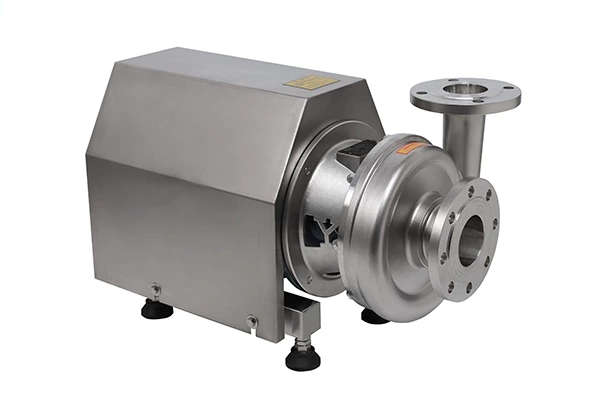
Emulsification Pump Material selection considerations
The basic requirements for a successful chemical centrifugal pump equipment are performance and life. Performance is the parameters of the pump: head, flow and power. Life is the total number of hours that one or more parts have been working under the condition of maintaining the allowed performance. It is mainly a measurement of the resistance of structural materials to corrosion, erosion or a combination of these two under actual operating conditions.
When selecting materials for centrifugal pump flow components, factors that need to be considered are: user experience, expected pump life (such as short-term or long-term use), continuous or continuous use, and conditions for pumping harmful or toxic liquids or liquids. The corrosiveness of the liquid varies depending on one or more of the following conditions: temperature, concentration, purity, speed, mixed solids and gases.
The initial cost of the selected material is usually considered first. However, operating costs, replacement costs, maintenance periods and repair costs will determine the actual cost of the pump during its life.
(1) Corrosiveness of the medium: The corrosion resistance of the material to the medium has a certain range. For example, 1Cr18Ni9 is resistant to corrosion by medium and dilute concentrations of nitric acid or organic acids, but not to corrosion by dilute sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid.
(2) Electrochemical corrosion: It is best to use the same metal material in the entire flow channel of the pump.
(3) Medium temperature: The material is brittle at very low temperatures and creeps at high temperatures; a certain material can resist corrosion by a certain medium at room temperature, but may not be resistant to corrosion by the medium at high temperatures; therefore, the material function should meet the temperature requirements of the transported medium.
(4) Economic efficiency: Different materials have different prices and machining functions. Therefore, when several materials meet the requirements of corrosion and temperature at the same time, materials with relatively low prices and good machining functions should be selected.
(5) Abrasiveness of solid particles: When the medium contains abrasive solid particles, wear-resistant materials should be selected.
(6) The bite between materials: For parts with relative motion, such as shaft and sleeve, bolt and nut, impeller seal ring and pump body seal ring, etc., the hardness of the two parts should be different when selecting materials, otherwise they are easy to bite or scratch each other during loading and unloading and operation.
(7) The size of the temperature difference on the same part: When the temperature difference of the same part is large during operation, such as when the pump cover is cooled when transporting high-temperature liquid, the temperature of the pump cover in contact with the medium is high and the expansion is large, and the temperature of the pump cover in contact with the cooling water is low and the expansion is small. Such parts should use materials with good plasticity to avoid cracks due to different expansion during operation.
(8) Parts that need to be welded: Parts that need to be repaired during casting, processing and use should use materials with better weldability, such as low carbon steel has better weldability than high carbon steel.
(9) Single-stage head is very high: For pumps with high single-stage head, the liquid flow rate is very high, and the flow-through parts should use high-strength steel that is resistant to erosion and cavitation, such as precipitation hardened stainless steel.
Industrial pump products are classified by use
Boiler feed pump: a pump that delivers water to the boiler. Multistage centrifugal pumps are often used. Common pump types are shown in the table below:
Condensate pump: a pump that pumps condensed water in the condenser. The pump is required to have high anti-cavitation performance.
Circulating water pump: a pump that forces water to circulate in a closed system, generally a low-lift, high-flow pump. Commonly used are single-stage, single-suction centrifugal pumps.
ISW horizontal pipeline centrifugal pumps
Hydraulic coal mining pump: a high-pressure pump used for hydraulic coal mining water guns.
Mine drainage pump: a pump that drains water from the mine to the outside.
Coal-water pump: a pump that transports coal-water mixture in coal mines.
Descaling pump: a high-pressure pump used to remove oxide scales during steel rolling in a steel mill.
Ballast pump: a pump that puts seawater into or out of the water tank in the ship according to the amount of cargo on board to keep the ship at a certain draft depth.
Tilt balance pump: a pump that moves the water in the left and right water tanks on the ship back and forth to maintain the balance of the hull.
Impurity pump: A general term for pumps that transport slurry containing solid particles.
Sand pump: A water pump that transports liquid containing sand.
Slurry pump: A pump that transports slurry.
Mud pump: A pump that transports mud. Common pump types are diaphragm pumps or screw pumps.