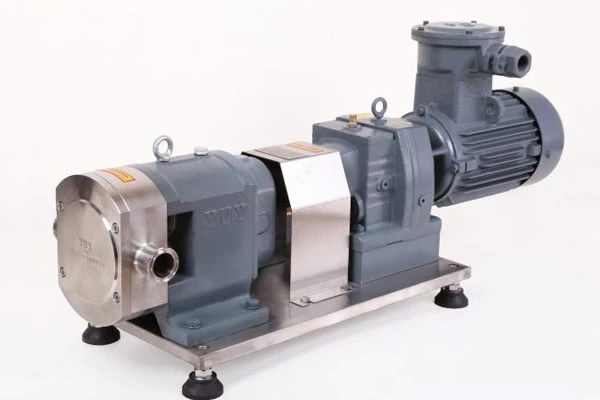
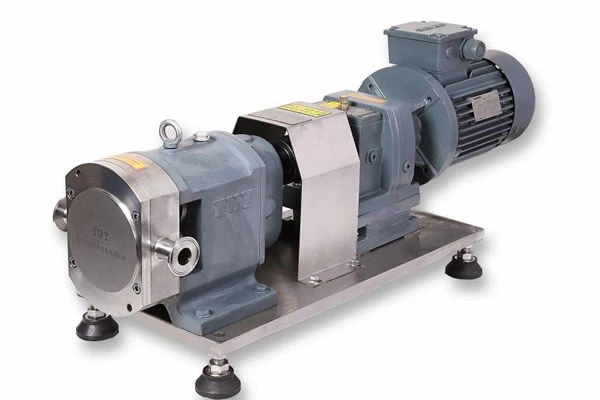
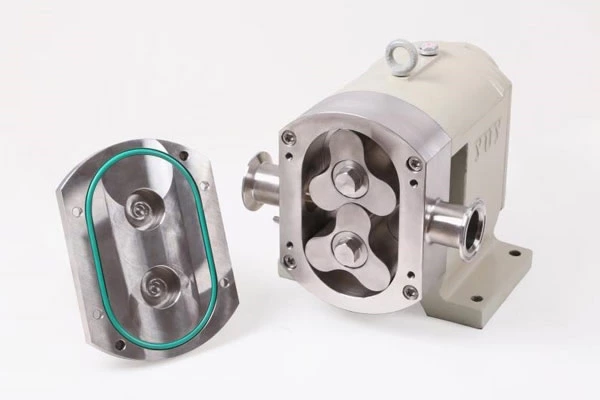
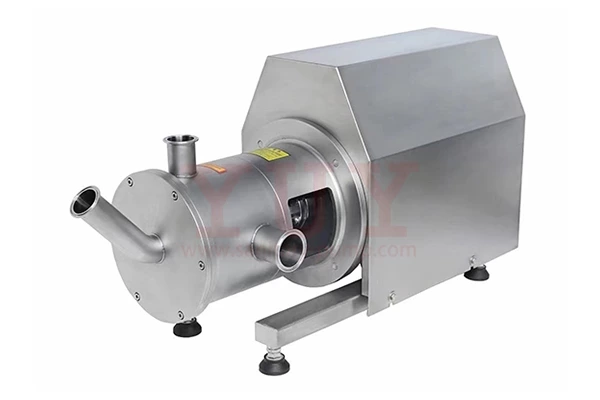
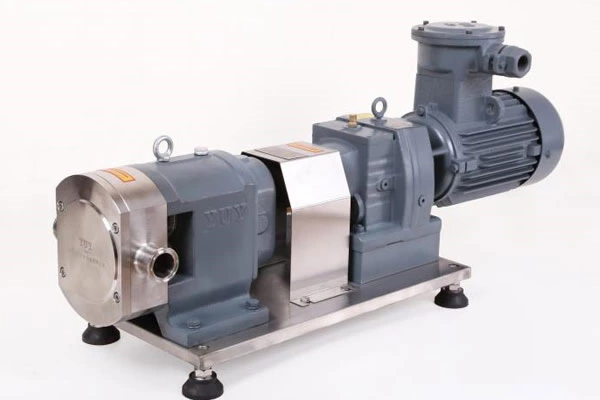
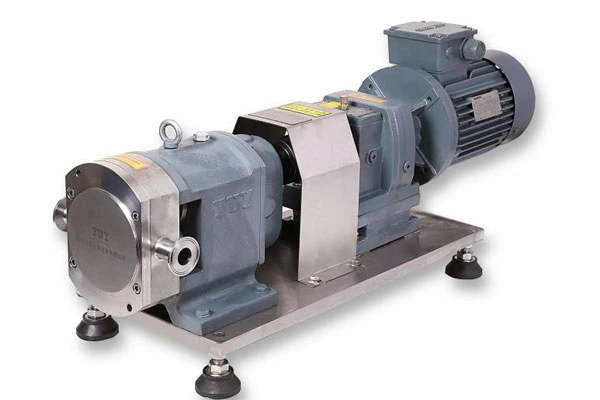
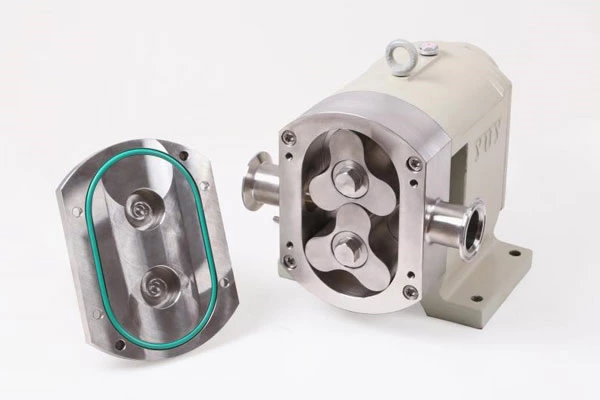
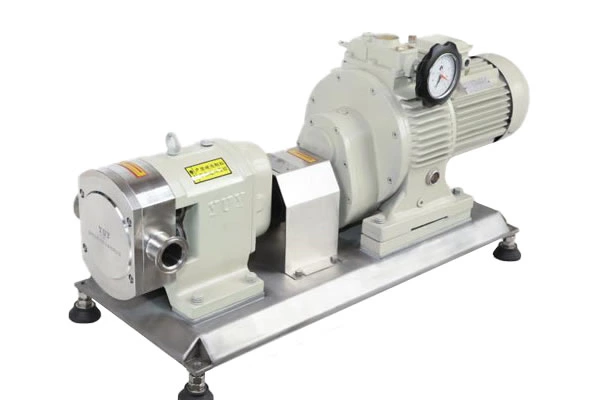
Common Failures Of Pipeline Pumps And Their Troubleshooting And Operation And Maintenance
Sanitary Rotary Lobe Pump Common fault phenomena, possible causes and corresponding troubleshooting methods are:
1. The water pump does not produce water.
Possible causes:
a. The inlet and outlet valves are not opened, the inlet and outlet pipes are blocked, and the flow channel impeller is blocked.
b. The motor movement direction is wrong, the motor is missing phase, and the number of revolutions is very slow.
c. The suction pipe is leaking.
d. The pump is not filled with liquid, and there is air in the pump chamber.
e. Insufficient inlet water supply, too high suction head, and bottom valve leakage.
f. The pipeline resistance is too large and the pump is improperly selected.
Corresponding troubleshooting methods:
a. Check and remove the blockage.
b. Adjust the direction of the motor and tighten the motor wiring.
c. Tighten the sealing surfaces and exhaust the air.
d. Open the pump cover or open the exhaust valve to exhaust the air.
e. Stop checking and adjusting (this phenomenon is prone to occur when using grid-connected tap water pipes and suction heads).
f. Reduce pipeline bends and reselect the pump.
2. The water pump flow is insufficient.
a. First check the cause according to 1.
b. The pipeline and pump flow channel impeller are partially blocked, scale is deposited, and the valve opening is insufficient.
c. The voltage is low.
d. The impeller is worn.
Corresponding elimination method:
a. First eliminate according to 1.
b. Remove the blockage and readjust the valve opening.
c. Stabilize the pressure.
d. Replace the impeller.
3. Excessive power.
Possible causes:
a. Use beyond the rated flow.
b. The suction range is too high.
c. Replace the bearing.
Corresponding elimination method:
a. Adjust the flow and close the outlet valve.
b. Lower the installation surface.
c. Replace the bearing.
4. Noise and vibration.