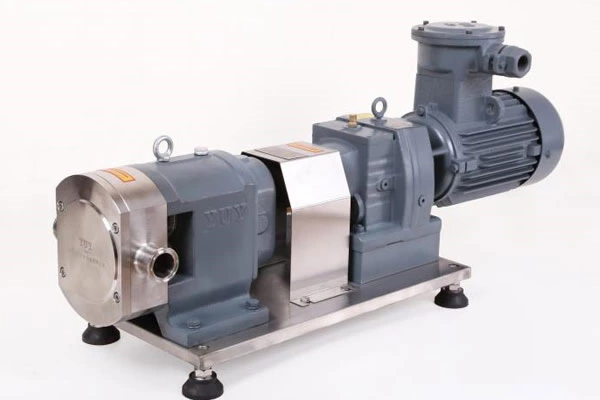
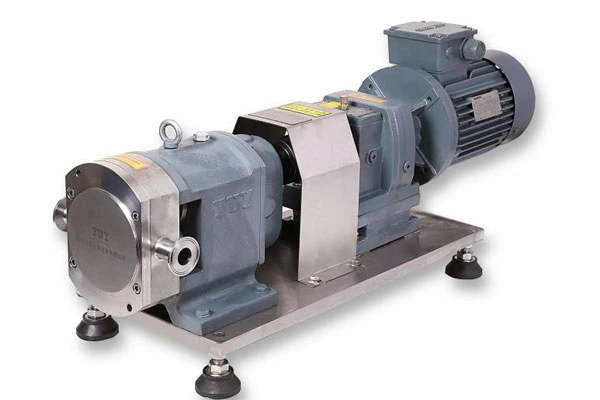
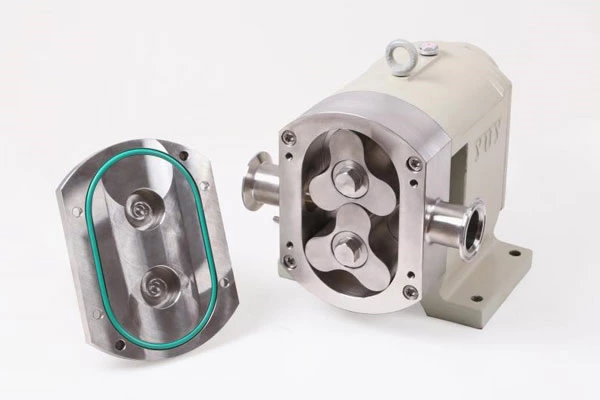
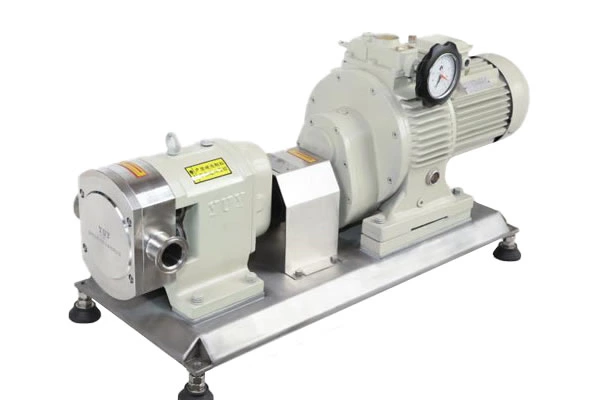
150 Technical Questions And Answers About Pumps To Help You Fully Understand Pumps
111. What kind of bearing is an unqualified bearing?
Answer: 1) Loss of original rotation accuracy, 2) Noise during operation, 3) Large rotation resistance.
112. What are the reasons for overheating of Emulsification Pump rolling bearings?
Answer: 1) Small axial reserved clearance of rolling bearings
2) Incorrect installation direction
3) Dry wear or looseness
4) Poor lubricating oil quality, insufficient oil or poor circulation
5) The oil ring is deformed and cannot carry oil.
113. What is the scrapping standard for rolling bearings for pumps (radial ball bearings)?
Answer: 1) The inner and outer ring raceways are peeled off, severely worn or cracked.
2) The rolling body is out of round or the surface is peeled off and cracked.
3) The cage is severely worn or deformed and cannot fix the rolling body.
4) There is noise or vibration when rotating, and there is braking phenomenon and reverse reversal when stopping.
5) The matching clearance of the bearing exceeds the maximum value of the specified clearance.
114. What causes the fish-scale peeling phenomenon on the track surface of the inner ring and outer ring of the bearing or the rolling surface of the rolling element?
Answer: 1) Excessive load, 2) Poor installation, 3) Foreign matter intrusion, unsuitable lubricant, 4) Unsuitable bearing clearance, 5) Poor precision of the shaft and bearing box, uneven rigidity of the bearing box, large deflection of the shaft, 6) Rust, corrosion points, scratches and indentations.
115. What are the performance aspects of bearing alloys?
Answer: 1) Low friction coefficient to reduce shaft wear; 2) High plasticity to make the shaft and bearing bushing run-in well; 3) Good thermal conductivity; 4) Sufficient compressive strength and fatigue strength.
116. What properties should high-speed rotating sliding bearings have?
Answer: 1) It should be able to withstand radial and axial loads; 2) It also requires a small friction coefficient; 3) Long life and stable and reliable operation at high speed.
117. What are the reasons for the vibration of rolling bearings?
Answer: 1) Random vibration transmitted by rolling elements. 2) Random vibration due to improper installation and lubrication. 3) Vibration from the outside of the bearing.
118. What are the assembly requirements for rolling bearings?
Answer: 1) The end face marked with the model on the bearing should be installed in a visible position for easy replacement.
2) The arc radius at the shaft neck or housing hole shoulder should be smaller than the arc chamfer radius of the bearing end face to ensure that the bearing is close to the shaft shoulder and the housing hole shoulder after assembly.
3) The bearing fixing device must be intact and reliable, with moderate tightening and reliable relaxation.
4) During assembly, keep it clean to prevent debris from entering the bearing;
5) After assembly, the bearing rotates flexibly and without noise, and the temperature rise generally does not exceed 50 degrees.
119. What are the common liner materials for sliding bearings? What are their characteristics?
Answer: 1) Gray cast iron, which is used in low speed, light load and no impact load conditions. Commonly used ones are HT15-33 and HT20-40.
2) Copper-based bearing alloy. Commonly used are ZQSn10-1 phosphorus tin bronze and ZQA19-4 aluminum bronze, which are suitable for working under medium speed, high turbidity and impact load conditions.
3) Oil-containing bearings: Generally, bronze and cast iron powders are pressed and formed with appropriate amounts of graphite, and then sintered at high temperature to form porous materials. Commonly used in low or medium speed, light load, and inconvenient lubrication.
4) Nylon. Commonly used are nylon 6, nylon 66 and nylon 1010. Nylon bearings have the advantages of good running and soft surface of debris after wear without damaging the journal, good corrosion resistance, poor thermal conductivity, and expansion after absorbing water.
5) Bearing alloy (Babbitt alloy). It is an alloy of tin, lead, copper, antimony, etc., with good wear resistance, but low strength. It cannot be made into a bearing alone, and is usually cast on a bearing base such as bronze, cast iron, and steel.
6) Three-layer load bearing material. There are two commonly used ones: polypropylene fluoride steel body composite material and polyoxymethylene steel body composite material.
120. What is the reason for the excessive temperature rise of rolling bearings?
Answer: 1) Impurities or dirt invade during installation and operation.
2) Use of inappropriate lubricants or insufficient lubricating oil.
3) Friction or loose fit between sealing devices, heat rings, bushings, etc. causes friction.
4) Improper installation, such as inner and outer ring deflection, non-concentric mounting seat holes, raceway deformation and improper clearance adjustment.
5) Wrong selection. When an unsuitable bearing is selected as a substitute, it will heat up due to overload or excessive speed.